GitHub Stars
0
User Rating
Not Rated
Favorites
0
Views
7
Forks
0
Issues
0
MCP-Auto-ML: Technical Project Report
1. Introduction
Automating the machine learning (ML) workflow is crucial for efficient, reproducible, and scalable data science. Traditional ML pipelines require repetitive code for data ingestion, cleaning, transformation, model training, hyperparameter tuning, and deployment, which distracts data scientists from analytical tasks. The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is designed as an open protocol to automate these processes, enabling Large Language Models (LLMs) and other agents to execute end-to-end ML workflows, including cloud deployment and database persistence. This report details the technical architecture, algorithms, and experimental results of MCP-Auto-ML, with a case study on the Heart Disease dataset from Kaggle[^1][^2][^3][^7].
Installation
Prerequisites:
- Python 3.8+
Required for all major data science and ML libraries. - pip
Python package manager for installing dependencies. - Kaggle API credentials
For programmatically downloading datasets from Kaggle. - AWS account and S3 bucket
For saving trained models. - MongoDB (local or remote)
For storing processed datasets. - Claude Desktop
For connecting the MCP server to LLM
Installation Steps:
- Clone the repository and set up a virtual environment:
git clone https://github.com/NaveenPrabakar/MCP-AutoML-Tool.git
cd MCP-AutoML-Tool
- Install Python dependencies:
pip install pandas scikit-learn matplotlib seaborn joblib boto3 pymongo kaggle fastapi uvicorn
- Configure Kaggle API:
- Download
kaggle.jsonfrom your Kaggle account. - Place it in
~/.kaggle/and set permissions:
- Download
mkdir -p ~/.kaggle
cp kaggle.json ~/.kaggle/
chmod 600 ~/.kaggle/kaggle.json
- Set up AWS credentials:
- Run
aws configureand enter your AWS Access Key, Secret Key, and region.
- Run
- Set up MongoDB:
docker run -d -p 27017:27017 --name mongo mongo:latest
Use your MongoDB connection string in the code.
6. Run the MCP server:
Use Claude Desktop to run the server
Tech Stack
| Component | Technology | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Data Handling | pandas | Data loading, manipulation, cleaning |
| ML Modeling | scikit-learn | Model training, evaluation, hyperparameter tuning |
| Visualization | matplotlib, seaborn | Data and result visualization |
| Storage | AWS S3 (boto3) | Saving trained models |
| Database | MongoDB (pymongo) | Storing processed datasets |
| Automation | FastAPI, MCP | Exposing tools via API and protocol |
| Data Source | Kaggle API | Automated dataset download |
| Serialization | joblib | Model persistence |
2. Problem Definition and Algorithm
2.1 Task Definition
Input:
- Tabular dataset (CSV), either uploaded or downloaded (e.g., from Kaggle)
- Specification of target variable and ML task (classification or regression)
Output:
- Trained and tuned ML model, persisted to AWS S3
- Cleaned, transformed dataset, persisted to MongoDB
- Performance metrics (e.g., accuracy, MSE)
Objective:
Automate the full ML workflow, minimizing manual intervention and code repetition, while ensuring reproducibility and cloud integration.
2.2 Algorithmic Workflow
The MCP-Auto-ML system is implemented as a set of asynchronous Python tools, orchestrated by a FastAPI-based server (FastMCP). The workflow is modular and extensible, supporting the following steps:
2.2.1 Data Ingestion
async def download_kaggle_dataset(name: str, kaggle_url: str) -> str:
# Extract dataset identifier, authenticate with Kaggle API, download, and cache DataFrame
- Extracts the dataset identifier from the Kaggle URL using regex.
- Downloads and extracts the first CSV file using the Kaggle API.
- Loads the data into a global cache (
dataset_cache).
2.2.2 Data Preview and Summary
async def preview_dataset(name: str, rows: int = 5) -> str:
# Returns first N rows in JSON for inspection
async def dataset_summary(name: str) -> str:
# Returns DataFrame.describe() output as JSON
- Enables rapid validation of data loading and initial statistical inspection.
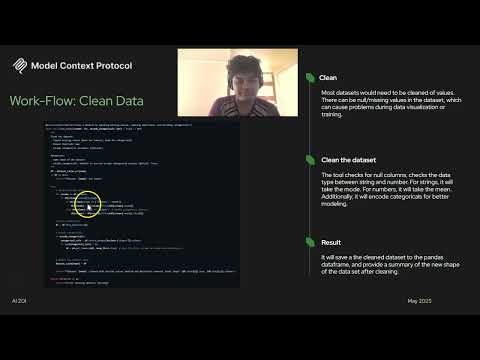
2.2.3 Data Cleaning
async def clean_dataset(name: str, encode_categoricals: bool = True) -> str:
# Impute missing values (mean/mode), remove duplicates, one-hot encode categoricals
- Numeric columns: impute with mean
- Categorical columns: impute with mode, optional one-hot encoding
- Removes duplicates and updates the cache
2.2.4 Data Visualization
async def visualize_data_distribution(name: str) -> str:
# Generates histograms for all numeric columns using matplotlib and seaborn
- Automates EDA by generating histograms for all numerical features
2.2.5 Data Transformation
async def transform_dataset(name: str, target: str, encode_categoricals: bool = True, normalize_numerics: bool = True) -> str:
# Label encodes categoricals (excluding target), standardizes numerics
- Categorical features: label encoding (excluding target)
- Numeric features: standard scaling
2.2.6 Model Training
async def train_model(name: str, target_column: str, model_type: str = "classification", model_name: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
# Trains model, returns accuracy or MSE
- Supports classification (Logistic Regression, Random Forest, SVM, KNN, Decision Tree) and regression (Linear Regression, Random Forest, SVM, Decision Tree)
- Splits data (80/20), trains model, evaluates on test set
2.2.7 Hyperparameter Tuning
async def hyperparameter_tuning(name: str, target: str, model_type: str = "classification", model_name: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
# GridSearchCV over model-specific parameter grid, returns best parameters
- Uses scikit-learn
GridSearchCVfor parameter optimization - Model-specific grids (e.g., C, penalty, solver for Logistic Regression)
2.2.8 Model and Data Persistence
async def save_model_to_s3(name: str) -> str:
# Serializes model with joblib, uploads to AWS S3
async def save_dataset_to_mongo(name: str) -> str:
# Converts DataFrame to dict, inserts into MongoDB collection
- Model: Saved as
.pklto S3 using boto3 - Data: Saved as JSON documents to MongoDB
3. Experimental Evaluation
3.1 Methodology
- Dataset: Heart Disease dataset from Kaggle (919 rows, 16 columns)
- Target Variable:
cp(chest pain type) - Task: Multiclass classification
- Evaluation Metric: Accuracy
- Baseline Model: Logistic Regression
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Grid search over C, penalty, solver
3.2 Results
| Step | Output/Metric |
|---|---|
| Data Download | 919 rows, 16 columns |
| Data Cleaning | 919 rows, 23 columns (categoricals one-hot encoded) |
| Data Transformation | 919 rows, 23 columns (label encoded, scaled) |
| Model Training | Logistic Regression, Accuracy = 0.9457 |
| Hyperparameter Tuning | Best: C=1, penalty='l2', solver='liblinear' |
| Model Persistence | S3 bucket: nflfootballwebsite/heart_disease_model.pkl |
| Data Persistence | MongoDB: dataset_heart_disease.data |
Visualization
- Histograms generated for all numerical features (e.g., age, trestbps, chol, thalch, oldpeak, ca, num)
- Confusion matrix available for classification models
3.3 Discussion
- The automated pipeline achieves high accuracy (94.57%) on the heart disease classification task.
- All steps are fully automated, requiring only a dataset URL and target specification.
- The workflow is robust to missing values, categorical features, and supports both cloud and database integration.
4. Related Work
- AutoML frameworks: Existing frameworks like Auto-sklearn and H2O.ai automate ML pipelines but are often monolithic and less extensible for LLM integration.
- MCP-Auto-ML distinguishes itself by exposing each step as an API/tool callable by LLMs or agents, enabling true automation and cloud orchestration beyond local execution[^3][^7].
- Cloud integration: Native support for AWS S3 and MongoDB persistence is a key differentiator.
5. Future Work
- Feature Engineering Automation: Current version does not automate feature engineering, which is highly context-dependent.
- LLM Integration: Extend support to additional LLMs (e.g., OpenAI GPT, Gemini) for broader agent compatibility.
- Expanded Model Support: Add more advanced models (e.g., XGBoost, deep learning).
- Automated Reporting: Generate full experiment reports and dashboards.
6. Conclusion
MCP-Auto-ML provides a modular, extensible, and fully automated machine learning pipeline, reducing manual coding and enabling rapid, reproducible model development. The protocol’s agent-friendly API design and cloud/database integration make it suitable for modern, production-grade ML workflows. High accuracy on the Heart Disease dataset demonstrates its practical utility. Future work will further expand automation and LLM compatibility[^1][^2][^3][^7].
Appendix: Poster Content (Technical)
Title: MCP-Auto-ML: Automated ML Pipeline via Model Context Protocol
Architecture Diagram:
- Data Ingestion → Cleaning → Visualization → Transformation → Model Training → Hyperparameter Tuning → Model/Data Persistence
Key Technologies:
- Python, pandas, scikit-learn, FastAPI, AWS S3, MongoDB, Kaggle API, matplotlib, seaborn
API Example:
# Download and cache dataset
await download_kaggle_dataset("heart_disease", kaggle_url)
# Clean and transform
await clean_dataset("heart_disease")
await transform_dataset("heart_disease", target="cp")
# Train and tune model
await train_model("heart_disease", target_column="cp", model_type="classification")
await hyperparameter_tuning("heart_disease", target="cp")
# Save model/data
await save_model_to_s3("heart_disease")
await save_dataset_to_mongo("heart_disease")
Performance:
- Logistic Regression on Heart Disease: 94.57% accuracy
Cloud Persistence:
- Model: AWS S3 (
nflfootballwebsite/heart_disease_model.pkl) - Data: MongoDB (
dataset_heart_disease.data)
Contact:
- Naveen Prbakar, May 2025
3
Followers
13
Repositories
0
Gists
0
Total Contributions